CAPITVLVM SECVNDVMSECOND CHAPTER
FAMILIA ROMANA ROMAN FAMILY
I
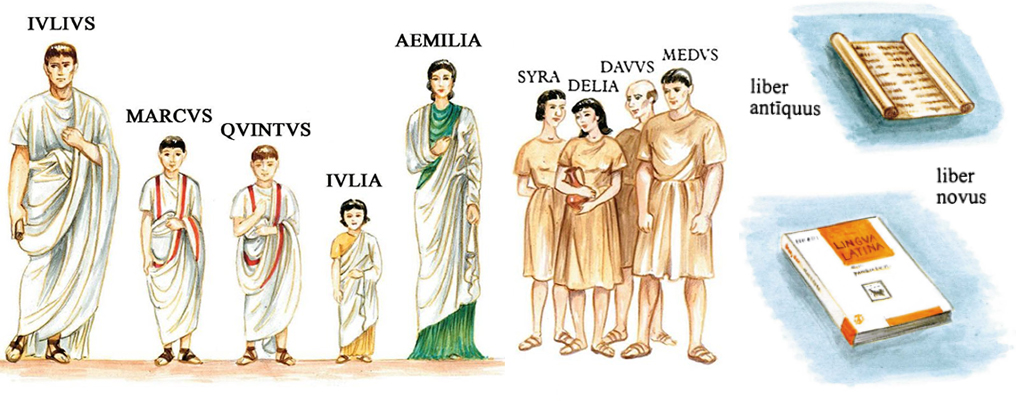
Iulius vir Romanus est. Aemilia femina Romana est. Marcus est puer Romanus. Quintus quoque puer Romanus est. Iulia est puella Romana.
Marcus et Quintus non viri, sed pueri sunt. Viri sunt Iulius et Medus et Davus. Aemilia et Delia et Syra sunt feminae. Estne femina Iulia? Non femina, sed parva puella est Iulia.
Iulius, Aemilia, Marcus, Quintus, Iulia, Syra, Davus, Delia Medusque sunt familia Romana. Iulius pater est. Aemilia est mater. Iulius pater Marci et Quinti est. Iulius pater Iuliae quoque est. Aemilia est mater Marci et Quinti et Iuliae. Marcus filius Iulii est. Marcus filius Aemiliae est. Quintus quoque filius Iulii et Aemiliae est. Iulia est filia Iulii et Aemiliae.
Quis est Marcus? Marcus puer Romanus est. Quis pater Marci est? Iulius pater Marci est. Quae est mater Marci? Mater Marci est Aemilia. Quae est Iulia? Iulia est puella Romana. Quae mater Iuliae est? Aemilia mater Iuliae est. Pater Iuliae est Iulius. Iulia filia Iulii est. Qui sunt filii Iulii? Filii Iulii sunt Marcus et Quintus. Marcus, Quintus Iuliaeque sunt tres liberi. Liberi sunt filii filiaeque. Marcus et Quintus et Iulia sunt liberi Iulii et Aemiliae. In familia Iulii sunt tres liberi: duo filii et una filia.
Estne Medus filius Iulii? Medus filius Iulii non est, Medus est servus Iulii. Iulius dominus Medi est. Iulius dominus servi est. Davus quoque servus est. Medus et Davus duo servi sunt. Iulius est dominus Medi et Davi. Iulius dominus servorum est et pater liberorum.
Julius is a Roman man. Emilia is a Roman woman. Marcus is a Roman boy. Quintus is also a Roman boy. Julia is a Roman girl.
Marcus and Quintes are not men, but are boys. The men are Julius, Medus, and Davus. Emilia, Delia, and Syra are women. Is Julia a woman? Julia is not a woman, but is a little girl.
Julius, Emilia, Macus, Quintus, Julia, Syra, Davus, Delia, and Medus are a Roman family. Julius is the father. Emilia is the mother. Julius is the father of Marcus and Quintus. Julius is also Julia's father. Emilia is the mother of Marcus, Quintus, and Julia. Marcus is the son of Julius. Marcus is Emilia's son. Quintus is also the son of Julius and Emilia. Julia is the daughter of Julius and Emilia.
Who is Marcus? Marcus is a Roman boy. Who is Marcus’s father? Julius is Marcus’s father. Who is the mother of Marcus? Marcus’s mother is Emilia. Who is Julia? Julia is a Roman girl. Who is the Julia’s mother? Emilia is Julia’s mother. Julia’s father is Julius. Julia is the daughter of Julius. Who are Julius’s sons? Julius’s sons are Marcus and Quintus. Marcus, Quintus, and Julia are three children. Children are sons and daughters. Marcus, Quintus, and Julia are the children of Julius and Emilia. In Julius’s family there are three children: two sons and one daughter.
Is Medus Julius’s son? Medus is not Julius’s son, Medus is Julius’s slave. Julius is Medus’s master. Julius is the slave’s master. Davus is also a slave. Medus and Davus are two slaves. Julius is Medus’s and Davus’s master. Julius is the master of the slaves and the father of the children.
II
Estne Delia filia Aemiliae? Delia non est filia Emiliae, Delia ancilla Aemiliae est. Aemilia domina Deliae est. Aemilia domina ancilla est. Syra quoque ancilla est. Delia et Syra duae ancillae sunt. Aemilia domina ancillarum est.
Cuius servus est Davus? Davus servus Iulii est. Cuius ancilla est Syra? Syra est ancilla Aemiliae.
Quot liberi sunt in familia? In familia Iulii sunt tres liberi. Quot filii et quot filiae? Duo filii et una filia. Quot servi sunt in familia? In familia sunt centum servi. In familia Iulii sunt multi servi, pauci liberi. Iulius est dominus multorum servorum.
'Duo' et 'tres' numeri sunt. 'Centum' quoque numerus est. Numerus servorum est centum. Numerus liberorum est tres. Centum est magnus numerus. Tres parvus numerus est. Numerus servorum est magnus Numerus liberorum parvus est. In familia Iulii magnus numerus servorum, parvus numerus liberorum est.
Medus servus Graecus est. Delia est ancilla Graeca. In familia Iulii sunt multi servi Graeci multaeque ancillae Graecae. Estne Aemilia femina Graeca? Aemilia non est femina Graeca, sed Romana. Iulius non vir Graecus, sed Romanus est.
Sparta oppidum Graecum est. Sparta, Delphi Tusculumque tria oppida sunt: duo oppida Graeca et unum oppidum Romanum est. In Gallia et in Italia magnus numerus oppidorum est. In Gallia est magnus numerus fluviorum. Fluvii Galliae magni sunt. Magnine sunt fluvii Africae? In Africa unus fluvius magnus est: Nilus; ceteri fluvii Africae parvi sunt. Suntne magnae insulae Graecae? Creta et Euboea duae insulae magnae sunt; ceterae insulae Graecae sunt parvae. –
Is Delia Emilia’s daughter? Delis is not Emilia’s daughter. Delia is Emilia’s handmaid. Syra is also a handmaid. Delia and Syra are two handmaids. Emilia is the mistress of the handmaids.
Whose slave is Davus? Davus is Julius’s slave. Whose handmaid is Syra? Syra is Emilia’s handmaid.
How many children are in the family? In Julius’s family there are three childreb. How many are sons and how many are daughters? Two sons and one daughter. How many slaves are in the family? There are a hundred slaves in the family. In Julius’s family there are many slaves, few children. Julius is the master of many slaves.
‘Two’ and ‘three’ are numbers. ‘One hundred’ is also a number. The number of slaves is one hundred. The number of children is three. One hundred is a large number. Three is a small number. The number of slaves is great. The number of children is small. In Julius’s family there is a large number of slaves, a small number of children.
Medus is a Greek slave. Delia is a Greek handmaid. In Julius’s family there are many Greek slaves and many Greek handmaids. Is Emilia a Greek woman? Amelia is not Greek, but a Roman woman. Julius is not Greek, but a Roman man.
Sparta is a Greek town. Sparta, Delphi, and Tusculum are three towns: two Greek towns and one Roman town. In Gaul and in Italy there are a great number of towns. In Gaul there is a great number of rivers. The rivers of Gaul are large. Are the rivers of Africa large? In Africa one river is large: the Nile; the other rivers of Africa are small. Are the islands of Greece large? Crete and Euboea are two large islands; the other islands of Greece are small. –
III
Quis est Cornelius? Cornelius dominus Romanus est. Iulius et Cornelius duo domini Romani sunt. Medus non est servus Cornelii. Medus servus Iulii est.
Cornelius: “Cuius servus est Medus?”
Iulius: “Medus servus meus est.”
Cornelius: “Estne Davus servus tuus?”
Iulius: “Davus quoque servus meus est. Servi mei sunt Medus et Davus et ceteri multi...”
Cornelius: “Estne Delia ancilla tua?”
Iulius: “Delia est ancilla mea, et Syra quoque ancilla mea est. Ancillae meae sunt Delia et Syra et ceterae multae. Familia mea magna est.”
Cornelius: “Quot servi sunt in familia tua?”
Iulius: “In familia mea sunt centum servi.”
Cornelius: “Quid?”
Iulius: “Numerus servorum meorum est centum.”
Cornelius: “Centum servi! Magnus est numerus servorum tuorum!”
Who is Cornelius? Cornelius is a Roman mistress. Julius and Cornelius are two Roman masters. Medus is not Cornelia’s slave. Medus is Julius’s slave.
Cornelius: “Whose slave is Medus?”
Julius: “Medus is my slave.”
Cornelius: “Is Davus your slave?”
Julius: “Davus is also my slave. My slaves are Medus and Davus and many others…”
Cornelius: “Is Delia your handmaid”
Julius: “Delia is my handmaid, and Syra is also my handmaid. My handmaids are Delia and Syra and many others. My family is large.”
Cornelius: “How many slaves are in your family?”
Julius: “In my family there are one hundred slaves.”
Cornelius: “What?”
Julius: “The number of my slaves is one hundred.”
Cornelius: “One hundred slaves! The number of your slaves is great!”
LIBER TVVS LATINVS
Ecce duo libri Latini: liber antiquus et liber novus. LINGVA LATINA est primus liber tuus Latinus. Titulus libri tui est 'LINGVA LATINA'. Liber tuus non antiquus, sed novus est.
In LINGVA LATINA sunt multae paginae et multa capitula: capitulum primum, secundum, tertium, cetera. 'IMPERIVM ROMANVM' est titulus capituli primi. Titulus capituli secundi est 'FAMILIA ROMANA'. In capitulo secundo sunt sex paginae. In pagina prima capituli secundi multa vocabula nova sunt: vir, femina, puer, puella, familia, cetera. Numerus vocabulorum Latinorum magnus est!
YOUR LATIN BOOK
Behold two Latin books: an old book and a new book. LINGUA LATINA is your first Latin book. The title of your book is ‘LINGUA LATINA.’ Your book is not old, but it is new.
In LINGUA LATINA there are many pages and many chapters: the first chapter, the second, the third, and so forth. ‘The Roman Empire’ is the title of the first chapter. The title of the second chapter is ‘Roman Family.’ In the second chapter there are six pages. On the first page of the second chapter there are many new words: vir, femina, puer, puella, familia, and so forth. The number of Latin words is large!
GRAMMATICA LATINA
Masculinum, femininum, neutrum
[A] 'Servus' est vocabulum masculinum
[B] 'Ancilla' est vocabulum femininum
[C] 'Oppidum' est vocabulum neutrum.
Exempla:
[A] Vocabula masculina: filius, dominus, puer, vir, fluvius, oceanus, numerus, liber, titulus. Masculinum: -us (-r).
[B] Vocabula feminina: femina, puella, filia, domina, insula, provincia, littera, familia. Femininum: -a.
[C] Vocabula neutra: oppidum, imperium, vocabulum, capitulum, exemplum, pensum. Neutrum: -um
Genetivus
[A] Masculinum:
Iulius dominus servi (Davi) est.
Iulius dominus servorum (Davi et Medi) est.
“Servi” genetivus est. 'Servorum' quoque genetivus est. “Servi” genetivus singularis est. 'Servorum' est genetivus pluralis. Genetivus: singularis -i, pluralis -orum.
[B] Femininum:
Aemilia domina ancillae (Syrae) est.
Aemilia domina ancillarum (Syrae et Deliae) est.
“Ancillae” genetivus singularis est. 'Ancillarum' est genetivus pluralis, Genetivus: singularis -ae. pluralis -arum.
[C] Neutrum:
D est prima littera vocabuli 'dominus'.
Numerus vocabulorum magnus est.
“Vocabuli” genetivus singularis est. 'Vocabulorum' est genetivus pluralis. Genetivus: singularis -i, pluralis -orum.
[D] Cetera vocabula
Cibus canis (Cerberi) in via est.
Numerus canum (Cerberi et multorum) magnus est.
“Canis” genetivus singularis est. 'Canum' est genetivus pluralis. Genetivus: singularis -is, pluralis -um.
LATIN GRAMMAR
Masculine, feminine, neuter
[A] Servus is a masculine word
[B] Ancilla is a feminine word
[C] Oppidum is a neuter word
Examples:
[A] Masculine words: son, master, boy, man, river, ocean, number, book, title. Masculine: -us (-r)
[B] Feminine words: woman, girl, daughter, island, province, letter, family. Feminine: -a
[C] Neuter words: town, empire, word, chapter, example, homework. Neuter: -um
Genitive
[A] Masculine:
Julius is the master of the slave (Davus).
Julius is the master of the slaves (Davus and Medus).
Servi is genitive. Servorum is also genitive. Servi is genitive singular. Servorum is genitive plural. Genitive: singular -i, plural -orum
[B] Feminine
Emilia is the mistress of the handmaid (Syra)
Emilia is the mistress of the handmaids (Syra and Delia)
Ancilae is genetive singular. Ancillarum is genitive plural. Genetive: singular -ae, plural -arum.
[C] Neuter
D is the first letter of the word dominus.
The number of words is large.
Vocabuli is genetive singular. Vocabulorum is genetive plural. Genetive: singular -i, plural -orum.
[D] Other words
The food of the dog (Cerberus) is in the road.
The number of dogs (Cerberus and many others) is great.
Canis is genetive singular. Canum is genetive plural. Genetive: singular -is, plural -um.
VOCABVLA
vir
femina
puer
puella
familia
pater
mater
filius
filia
liberi
servus
dominus
ancilla
domina
liber
titulus
pagina
antiquus
novus
ceteri
meus
tuus
centum
duo, duae
tres, tria
quis?
quae?
qui?
cuius?
quot?
VOCABULARY
man
woman
boy
girl
family
father
mother
son
daughter
children
slave
master
maid
mistress of a family; wife
book
title
page
old
new
the others; the rest
my
your
100
two
three
who? (masculine)
who? (feminine)
who? (plural)
whose?
how many?